Insyde® Software BlinkBoot® is a UEFI-based boot loader that leverages Intel® Firmware Support Package (Intel® FSP) to deliver simple, fast and scalable firmware solutions for Internet of Things (IoT) platforms. (v.2, May 2016). Download links are directly from our mirrors or publisher's website, insyde bios flash tool torrent files or shared files from free file sharing and free upload services, including Rapidshare, MegaUpload, YouSendIt, Letitbit, DropSend, MediaMax, LeapFile, MyOtherDrive, HellShare, HotFile, FileServe or MediaFire, are not allowed! Just download the appropriate zipped BIOS file, unpack it, rename it to something simple like bios.bin (Award, Phoenix - Award) or bios.rom (AMI, Phoenix) and use the suitable flash tool listed below. After updating the BIOS successfully shut down the PC, disconnect the A/C power cable (or switch off power supply) and make a Clear CMOS. Download google.com InsydeFlash Application. If theres nothing odd and even voltages loook correct im back to zero. Select the file version you need to download, this tool will automatically download a complete file for you. I tried again to restart the computer and it seems to be fine now. Tools for every major stage of the system development lifecycle. Our EDK-II based UEFI BIOS tools packages address the critical needs of every major stage of the system development lifecycle including product development, validation, provisioning, customization and post-production end-user requirements, and Insyde Software provides several unique tools to serve the development needs of each stage.
TQ provides tools from Insyde® for the UEFI BIOS which allows the customization of the BIOS.
Please Note: The following Tools are only available on request.
For further Information please contact Support.
- H2OFFT™ (Firmware Flash Tool) for performing BIOS Update
- H2OUVE™ (UEFI Variable Editor) to customize default BIOS Options
- H2OLRT™ (Logo Replacement Tool) for a customized boot logo
- H2OSDE™ (SMBIOS Data Editor) to facilitate easy modification of any SMBIOS (DMI) field
- H2OEZE™ (Easy Binary Editor) to edit binaries in the BIOS, including Option ROMs, driver binaries, logos, and Setup values
Further Tools are only available from Insyde®:
- H2ODDT™ (Developer Debug Tool) for source code level Diagnostic and Debugging
- H2OPCM™ (Power Cycle Manager) for assisting in power-cycling the system while watching for initialization failures
- H2OELV™ (Event Log Viewer)
Using BIOS Tools
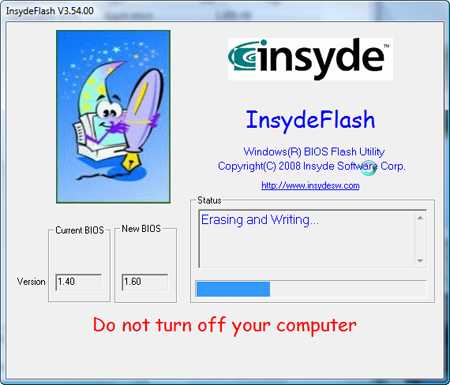
H2OFFT (Firmware Flash Tool)
H2OFFT (Firmware Flash Tool) to perform BIOS updates under supported OS environment.
Prerequisites
- FAT formatted USB stick with at least 32 MB of free storage space
1. Unzip BIOS-Tools ZIP file and copy the following to the USB stick:
- Insyde Firmware Flash Tool H2OFFT-Sx64.efi (BIOS-Tools → H2OFFT (Firmware Flash Tool) → UEFI-Shell → InsydeH2OFFT_x86_EFI_Package_* → InsydeH2OFFT_x86_EFI_* → X64 → H2OFFT-Sx64.efi)
2. Insert the prepared USB Stick to a Starterkit USB port
3. Boot up the system and navigate into the EFI Shell (Boot Manager > Internal EFI Shell)
4. After starting the EFI Shell switch path to the USB stick by typing fs0:.This depends on the amount of conected mass storage devices; with command ls you can check the content of the path.
5. The following command examples shows how to use the H2OFFT Tool.
1. Unzip BIOS-Tools ZIP file and copy the following to the USB stick:
- Insyde Firmware Flash Tool folder InsydeH2OFFT_x86_WIN64_* (BIOS-Tools → H2OFFT (Firmware Flash Tool) → Windows → X64 → InsydeH2OFFT_x86_WINx64_*)
- Copy appropriate BIOS file for your TQ module to the folder InsydeH2OFFT_x86_WIN64_*
2. Insert the prepared USB Stick to a Starterkit USB port
3. Boot up the system and run Command Prompt as administrator
4. Switch path to the InsydeH2OFFT_x86_WIN64_* folder.
5. Following generic commands shows how to start the BIOS Update for TQMx86 modules.
1. Unzip BIOS-Tools ZIP file and copy the following to the USB stick:
- Insyde Firmware Flash Tool folder InsydeH2OFFT_x86_LINUX64_* (BIOS-Tools → H2OFFT (UEFI Variable Editor) → Linux → X64 → InsydeH2OUVE_x86_LINUX64_*)
2. Insert the prepared USB Stick to a Starterkit USB port
3. Boot up the system and open terminal
4. Switch path to the InsydeH2OFFT_x86_LINUX64_* folder
5. Extract tar package tar -xvf InsydeH2OFFT_x86_LINUX64_portable_*.tar.bz2
6. Install H2OFFT Tool sudo dpkg -i InsydeH2OFFT_x86_LINUX64_*.deb
- If errors occur during driver installation, build driver manually:
7. Run following generic commands shows how to start the BIOS Update for TQMx86 modules.
H2OUVE (UEFI Variable Editor)
The H2OUVE (UEFI Variable Editor) allows to edit setup settings and variable data of the BIOS Image.
Prerequisites
- FAT formatted USB stick with at least 32 MB of free storage space
1. Unzip BIOS-Tools ZIP file and copy the following to the USB stick:
- Insyde UEFI Variable Editor H2OUVE-Sx64.efi (BIOS-Tools → H2OUVE (UEFI Variable Editor) → UEFI-Shell → InsydeH2OUVE_x86_EFI_* → H2OUVE-Sx64.efi)
2. Insert the prepared USB Stick to a Starterkit USB port
3. Boot up the system and navigate into the EFI Shell (Boot Manager > Internal EFI Shell)
4. After starting the EFI Shell switch path to the USB stick by typing fs0:.This depends on the amount of conected mass storage devices; with command ls you can check the content of the path.
5. The following command examples shows how to use the H2OUVE Tool.
1. Unzip BIOS-Tools ZIP file and copy the following to the USB stick:
- Insyde UEFI Variable Editor folder InsydeH2OUVE_x86_WINx64_* (BIOS-Tools → H2OUVE (UEFI Variable Editor) → Windows → X64 → InsydeH2OUVE_x86_WINx64_*)
- Copy appropriate BIOS file for your TQ module to the folder InsydeH2OUVE_x86_WINx64_*
2. Insert the prepared USB Stick to a Starterkit USB port
3. Boot up the system and run Command Prompt as administrator
4. Switch path to the InsydeH2OUVE_x86_WINx64_* folder.
5. Following command examples shows how to use the H2OUVE Tool.
1. Unzip BIOS-Tools ZIP file and copy the following to the USB stick:

- Insyde UEFI Variable Editor folder InsydeH2OUVE_x86_LINUX64_* (BIOS-Tools → H2OUVE (UEFI Variable Editor) → Linux → X64 → InsydeH2OUVE_x86_LINUX64_*)
2. Insert the prepared USB Stick to a Starterkit USB port
3. Boot up the system and open terminal
4. Switch path to the InsydeH2OUVE_x86_LINUX64_* folder
5.Extract package tar -xvf InsydeH2OUVE_x86_LINUX64_portable_.tar.bz2
6. Install H2OUVE Tool sudo dpkg -i InsydeH2OUVE_x86_LINUX64_*.deb
- If errors occur during driver installation, build driver manually:
7. Run following generic commands shows how to start the BIOS Update for TQMx86 modules.
H2OLRT (Logo Replacement Tool)
This instructions guide you through the procedure of replacing the Bootlogo in EFI-Shell, Windows and Linux.
The H2OLRT (Logo Replacement Tool) generates a BIOS file that contains the desired Boot Logo instead of the TQ Logo.
Prerequisites
- FAT formatted USB stick with at least 32 MB of free storage space
1. Unzip BIOS-Tools ZIP file and copy the following to the USB stick:
- Insyde Boot Logo Replacement Tool H2OLRT-Sx64.efi (BIOS-Tools → H2OLRT (Logo Replacement Tool) → UEFI-Shell → InsydeH2OLRT_x86_EFI_* → H2OLRT-Sx64.efi)
- The new Boot Logo Picture formated as *.jpg (e.g. picture.jpg)
2. Insert the prepared USB Stick to a Starterkit USB port
3. Boot up the system and navigate into the EFI Shell (Boot Manager > Internal EFI Shell)
4. After starting the EFI Shell switch path to the USB stick by typing fs0:.This depends on the amount of conected mass storage devices; with command ls you can check the content of the path.
5. The following shows how to start the Logo Replacement.
H2OLRT-Sx64.efi Variable description
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| <SrcBIOSImageName> | BIOS file in which the logo should be replaced |
| <LogoImagePathName> | Path and name of the replacement picture |
| <IndexNum> | Default index, where the picture must be stored. TQMxE39S = 1 |
| <ConvertNum> | 0 = keep original image's format and dimension. 1 [default] = auto convert the image's format and dimension. |
| <OutBIOSImageName> | path and name of the generated BIOS file |
H2OSDE (SMBIOS Data Editor)
The tool H2OSDE (SMBIOS Data Editor) facilitates easy modifications of any SMBIOS (DMI) field.

Prerequisites
- FAT formatted USB stick with at least 32 MB of free storage space
1. Unzip BIOS-Tools ZIP file and copy the following to the USB stick:
2. Insert the prepared USB Stick to a Starterkit USB port
3. Boot up the system and navigate into the EFI Shell (Boot Manager > Internal EFI Shell)
4. After starting the EFI Shell switch path to the USB stick by typing fs0:.This depends on the amount of conected mass storage devices; with command ls you can check the content of the path.
5. The following command examples shows how to use the H2OSDE Tool.
- navigate to the H2OSDE program path and open the program GUI.exe
Alternatively, the program can also be executed in the windows command prompt:
- navigate to the H2OSDE program path and run following command:
Alternatively, the program can also be executed in the terminal: